Unplanned downtime costs companies millions of dollars every year, stemming from machinery failures, accidental spills, natural disasters, software bugs, and countless other causes. Moreover, this issue generates losses across multiple fronts—revenue losses, idle personnel, repair costs, inventory adjustments, and production line restarts.
Fundamentals of Predictive Maintenance
Today, one of the most effective ways to reduce downtime is through predictive maintenance. Predictive maintenance involves using a facility's operational data to detect anomalies and identify signs of potential failures about to occur in machinery. This mechanism emerges as the natural evolution of equipment care and preservation in the industrial sector, driven by our rapidly growing capacity to process and analyze data.
Unlike preventive maintenance, which is scheduled at regular intervals without considering the current state of machinery, predictive maintenance relies on continuous monitoring of equipment operating conditions to predict when maintenance will be needed. This approach enables precise interventions just before breakdowns occur, thereby avoiding the cost and lost time associated with unexpected failures.
Benefits of predictive maintenance:
- Reduced operational costs: By avoiding unplanned downtime, you save on emergency repair costs, which tend to be quite high.
- Improved safety and reliability: Preventing failures before they occur reduces the risk of accidents and increases confidence in machinery operability.
- Optimized equipment lifespan: Maintenance is performed only when necessary, avoiding the additional wear associated with excessive or insufficient maintenance.
- Efficient maintenance planning: By predicting when interventions will be needed, companies can better organize their resources and personnel.
Frequency Analysis: A Key Tool
But how is machinery data collected and analyzed? One of the most effective methods is performing analysis on equipment vibrations, measuring displacement, velocity, and acceleration across its three axes of movement. For this, specialized hardware is used, which is installed on each machine and collects the information. This hardware, in complex cases, can be custom-manufactured according to corporate or machine-specific needs, while at other times, it can be a generic device that can be acquired through companies like Treon or NCD.
Once data is collected, mathematical analyses are performed in both time and frequency domains to find anomalies in the machine's natural behavior and detect small failures that could trigger downtime for the production line. This is made possible by a comprehensive digital infrastructure that allows you to collect, store, process, and visualize massive amounts of data on a daily basis, using different diagnostic models that help monitor the health of your assets and identify more than 40 possible failures so you can take action and perform adequate maintenance before it's too late.
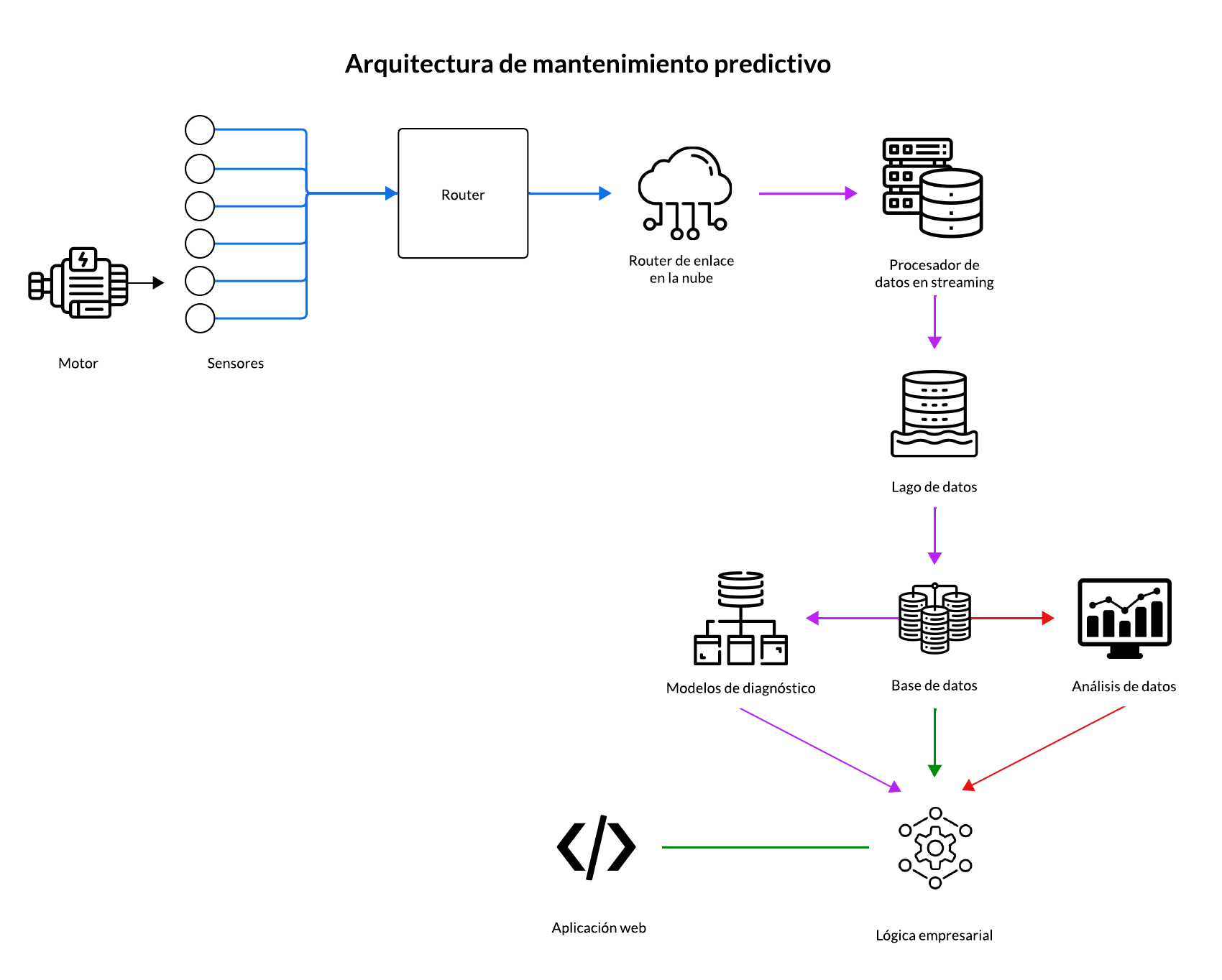
The mathematical tools that enable us to visualize and analyze the frequency domain were something that radically revolutionized the engineering landscape. These mathematical instruments allow us to analyze the amplitude of each frequency in a signal. That is, if you have a motor operating at 100 revolutions per second, you'll most likely notice, through this tool, a high amplitude at the 100 Hz frequency. This is important because each machine, under different conditions, dictates different values in this frequency domain, and therefore, you can find faults in your machinery through anomalies in this set of values.
Advantages of vibration analysis:
- Efficient maintenance scheduling: By knowing the exact state of equipment, companies can better plan maintenance shutdowns, minimizing impact on production.
- Early fault detection: Identifies abnormalities in critical machinery parts, such as bearings, gears, and shafts, before they result in failures.
- Precise diagnostics: Helps determine the nature and severity of the problem, enabling a more effective and specific response.
Vibration analysis, therefore, not only acts as a harbinger announcing future problems, but as a compass guiding toward the most effective preventive action, ensuring that predictive maintenance fulfills its promise of keeping machinery in optimal operation and downtime to a minimum.
Implementation
To implement a vibration analysis solution in a company, there are mainly three paths: developing the capability internally, hiring an external R&D team to customize and implement the solution, or acquiring and licensing existing software from a reliable provider. Each option has its specific advantages and requirements.
Option 1: Internal Development
Internal implementation involves assessing the company's needs, forming a team, acquiring vibration analysis equipment, and developing internal competencies for system operation and maintenance. This option offers greater control over the process and solution customization, but requires a significant investment in time, resources, and personnel training.
Advantage: The organization has total control over implementation, personnel, and development timeline.
Disadvantage: Requires a significant investment in qualified personnel, technology, and training.
Option 2: Hiring an External R&D Team
An efficient alternative is outsourcing the project to a specialized R&D team. This option allows the company to benefit from experience and advanced technical knowledge without having to worry about implementation details. The contracting company can specify its requirements and expectations, and the external team will handle everything, from development through commissioning and post-implementation support. This collaboration enables customizing the solution to fit the company's operational and strategic needs, from sensor selection to integration with existing systems and data analysis.
How it works:
- Select a Provider: The company must select an R&D service provider with extensive experience in developing and implementing these types of projects.
- Project Definition: The project scope is defined, including objectives, timeline, and expected deliverables, in collaboration with the chosen provider.
- Financial Agreement: The company and provider agree on a financing model, which may include stage payments, a flat rate for the complete project, or a payment model based on success and results obtained.
- Implementation, Adoption, and Support: The external R&D team implements the solution, performs necessary testing and adjustments, and provides training and support to the company's personnel.
Advantage: The return on investment often justifies this expense due to reduced downtime and increased operational efficiency.
Disadvantage: May represent a more significant initial cost compared to basic internal solutions or software licenses.
Option 3: Acquiring an Existing Software License
The final option is acquiring a license for already-developed vibration analysis software. This option is the fastest to implement and requires fewer internal resources, but may offer less flexibility in terms of customization.
How it works:
- Software Evaluation: The company evaluates different software solutions available in the market, considering factors such as functionality, ease of use, compatibility with existing hardware, and cost.
- Purchase and License: Once the software is selected, the company acquires the necessary licenses, and the software provider offers training and technical support.
- Integration and Use: The software is integrated into the company's existing systems, and personnel receive training to begin using the tool in daily operations.
Advantage: It's a very fast and simple way to start implementing preventive maintenance in the company and with a lower initial cost than the other options.
Disadvantage: Licensed software may not offer all the specific functionalities the company needs or may limit integration with other systems.
Conclusion
In a world where unplanned downtime can mean millions of dollars in losses for companies, adopting predictive maintenance strategies and vibration analysis presents itself as a crucial solution. These techniques not only help avoid costly operational interruptions but also improve safety, reliability, and machinery lifespan. Through the use of operational data and frequency analysis, companies can detect anomalies and prevent failures before they occur, ensuring efficient maintenance scheduling and minimizing impact on production.
Exploring the adoption of predictive maintenance and vibration analysis technologies is a crucial step toward operational optimization. The objective is clear: minimize downtime and maximize productivity. Taking the initiative today represents a more productive and profitable tomorrow.
